Cart
Discount: 0.00 EUR
Discount: 0.00 EUR
Digital Skipper |1/09, 2021
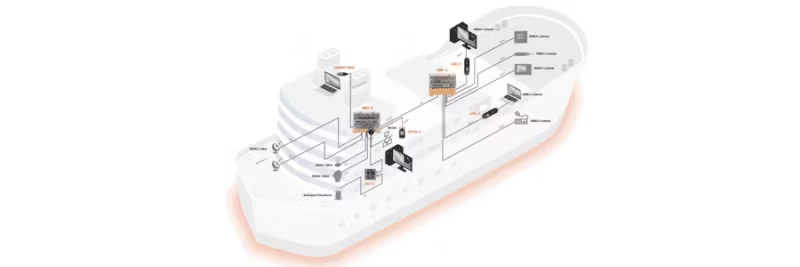
NMEA 0183 is a standard developed over 20 years ago to enable communication between marine electronic equipment and navigation computers. It has become the most common method for marine devices to share important data.
The standard defines:
NMEA 0183 is a digital data transfer method that uses binary signals (1s and 0s) to represent information. It has evolved from older standards (NMEA 0180 and 0182), but these are not compatible with NMEA 0183. The newer NMEA 2000 standard is completely different and requires a gateway, such as Actisense NGW-1, for conversion between the systems.
An NMEA 0183 bus always has one talker but can have multiple listeners. The latest versions (v2 onwards) follow the RS422 standard with low-voltage signaling (+5/0 V), making them compatible with modern equipment. Older devices, however, can use up to ±15 V, which requires the receiving equipment to be opto-isolated to avoid damage and interference.
All NMEA 0183 data is sent as printable ASCII text, allowing it to be displayed in terminal programs like HyperTerminal. Note that NMEA 0183-HS or v3 is not compatible with NMEA 2000. For conversion between these standards, a gateway like Actisense NGW-1 is required.
NMEA 0183 has evolved over time, making connections between older and newer devices complicated. Older devices use ground as a return, while newer devices use differential signaling. Incorrect connection can cause overheating and damage.
Actisense has implemented ISO-Drive outputs on all new products to provide the necessary isolation and safety. If the ISO-Drive "B" wire is connected to ground, no current will flow, making the system safe even when mixing different manufacturers.