Cart
Discount: 0.00 SEK
Discount: 0.00 SEK
Digital Skipper |26/03, 2020

Choosing the right cable dimension for your boat installation is crucial for safety and function. Incorrect cable choice can lead to:
Therefore, it is important to follow both rules of thumb and the ISO standard for electrical systems in recreational boats.
According to ISO 13297:2021, the following guidelines apply for voltage drop during boat installation:
These are not just recommendations – they are international standards to avoid risks and ensure optimal operation.
Calculating the correct cable cross-section can be complicated, but with the Victron Energy cable calculator in the Victron Toolkit app, it becomes easy. The calculator takes into account:
The app works for both AC and DC installations and helps you comply with ISO standards.
A rule of thumb is:
These values comply with ISO 13297:2021.
Do you suspect that the cable dimensions are incorrect? Perform spot checks on some consumers. This can reveal if adjustments are needed to avoid problems.
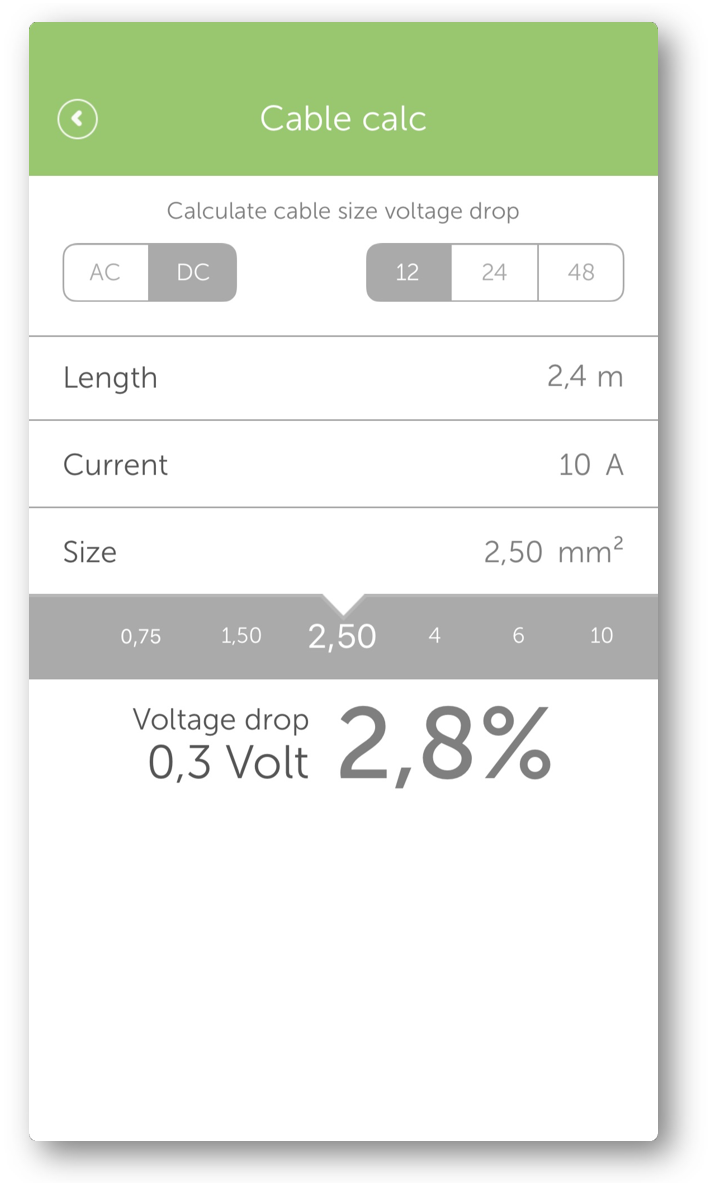
A consumer of 10 A with a cable length (total length for both positive and negative) of 2.4 m needs a cable of 2.5 mm² to keep the voltage drop below 2.8% (equivalent to 0.3 V).
Below the values: