Cart
Discount: 0.00 NOK
Discount: 0.00 NOK
Digital Skipper |14/04, 2020
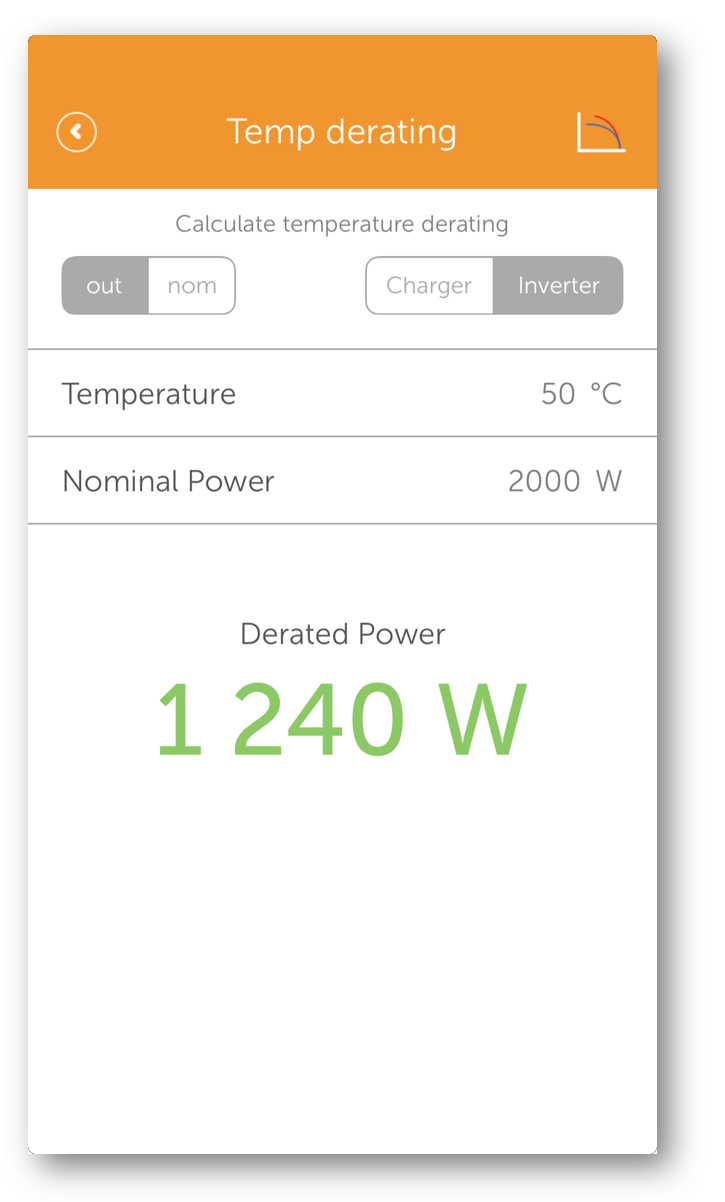
Have you noticed that your charger or inverter isn't delivering the power stated in the specification? Or wondered why the coffee machine doesn't work while underway – even though the inverter should be able to handle it?
The explanation is simple: the temperature in the installation space directly affects the power.
Most specifications apply at 25 °C. But if your equipment is mounted in the engine room, the temperature while underway can be around 50 °C – and that changes everything.
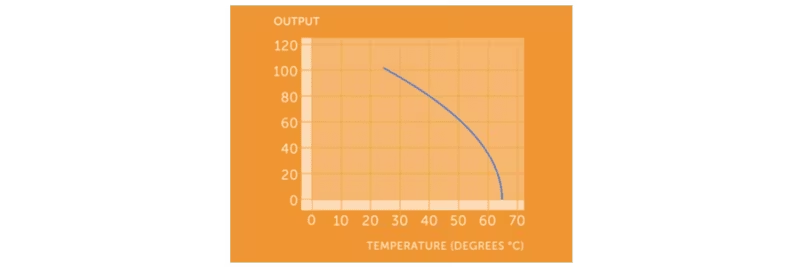
Example of power loss:
Even at 30 °C on a warm summer day, the difference is noticeable:
Use Victron Toolkit and the Temp Derating function to simulate how temperature affects power and plan your installation accordingly.